Haseung Jun
J
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
J
Jeanne Stansak
AP Macroeconomics 💶
99 resourcesSee Units
Interest Rates
Nominal interest rates are the interest rates that have not been adjusted for the impact of inflation. Real interest rates are those that have been adjusted for the impact of inflation. The equation for nominal interest rates is real interest rate + inflation. The equation for the real interest rate is the nominal interest rate - inflation.

nominal interest rate = real interest rate +inflation
Chart
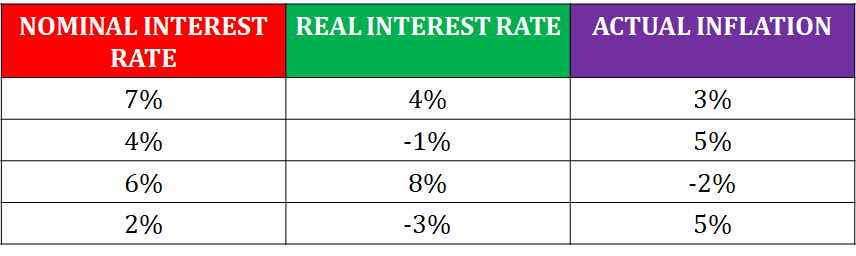
Nominal Interest Rates
The nominal interest rate is what is said to be the interest rate. Banks, investments and debt issuers advertise at this interest rate. It's always higher than the real interest rate because it doesn't take into account the continual loss of value in money.
Real Interest Rates
This is what is adjusted to inflation. This is a similar concept to nominal GDP and real GDP. With this, investors can estimate actual returns for later on, when the value of money may have changed. This can be negative if inflation is higher than the nominal rate, but most of the time, it's a better way to predict your real returns.
Predictions
Economists can make predictions based on other economic indicators and what the expected inflation rate is going to be. Lending institutions factor in expected inflation when they set the nominal interest rates on loans or different interest-bearing accounts. If the inflation rate is higher than what the expected inflation rate is, the real interest rate will decrease. If the inflation rate is lower than the expected inflation rate, the real interest rate will increase.
Lenders and borrowers establish these interest rates through expected inflation and the through finding the equilibrium within the market.
You'll learn later that there's a whole market for loanable funds, and the interest rate is often decided by the intersection of supply and demand. I guess supply and demand just never goes away, right? 😅
Browse Study Guides By Unit
💸Unit 1 – Basic Economic Concepts
📈Unit 2 – Economic Indicators & the Business Cycle
💲Unit 3 – National Income & Price Determination
💰Unit 4 – Financial Sector
⚖️Unit 5 – Long-Run Consequences of Stabilization Policies
🏗Unit 6 – Open Economy - International Trade & Finance
🤔Exam Skills
📚Study Tools

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.