1.1 Introduction to Maps and Types of Maps
8 min read•june 18, 2024
Riya Patel
Sana Fatah
Riya Patel
Sana Fatah
AP Human Geography 🚜
320 resourcesSee Units
Early Maps vs Contemporary Maps
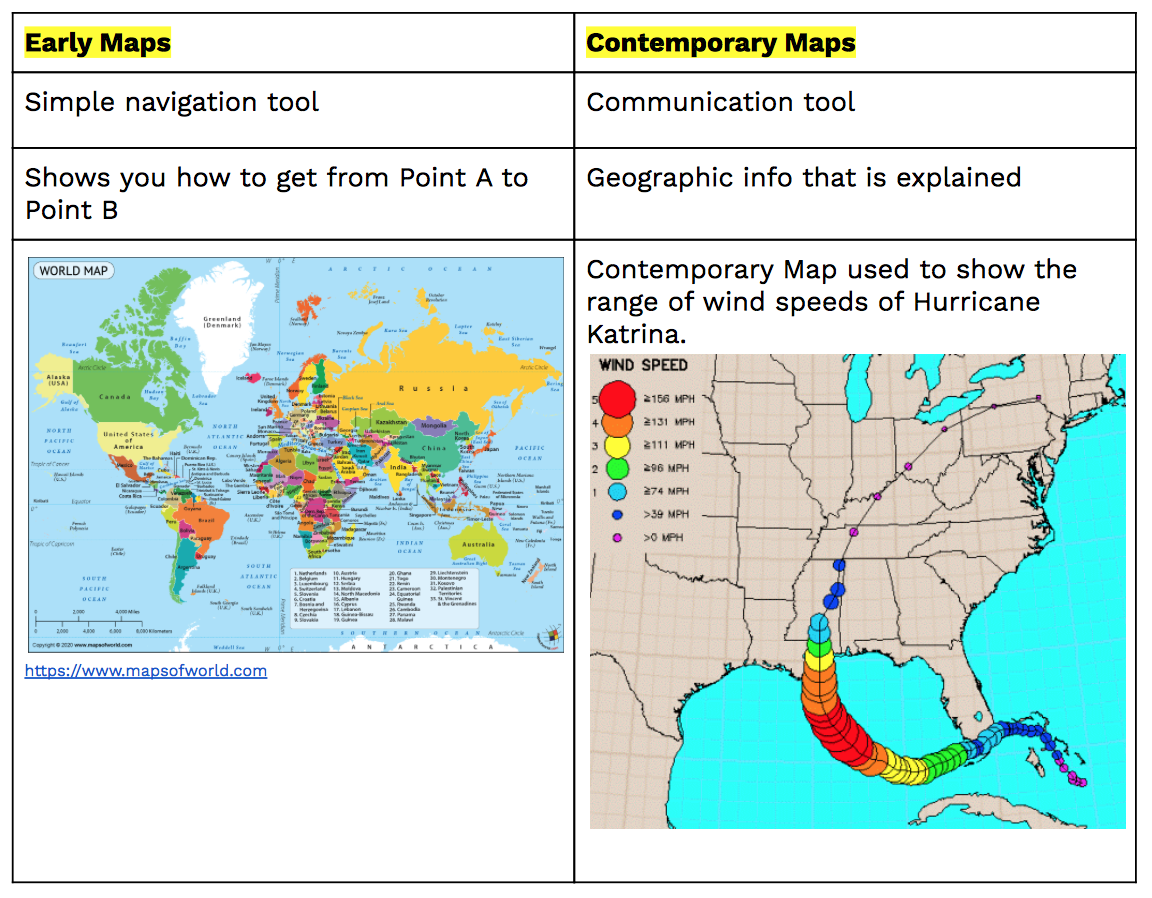
Map Scale and Projection
Have you ever seen a map the size of America? Or the size of the world? No? Then how are maps accurate if they are not the same size as the area they are representing? That’s where scaling comes into play.
A map scale is a way to represent the relationship between distances on a map and the actual distances on the ground.
Map scales can vary greatly, depending on the size and purpose of the map. Large-scale maps, such as those used for city or street maps, have a small scale and show a lot of detail. Small-scale maps, such as world or regional maps, have a large scale and show less detail but cover a larger area.
Map scales are an important consideration when using maps, as they affect the accuracy and level of detail that can be represented on the map. It is important to choose the appropriate scale for the purpose of the map and the amount of detail needed.
The three most common forms are:
- Ratio
- 1 : 25,000
- The number on the left of the ratio is always the units of distance on the map
- The number on the right is always the unit of distance on Earth’s surface
- Every 1 inch on this map represents 25,000 actual inches on Earth’s surface.
- Written scale
- “1 inch equals 1 mile”
- Explains the relationship in words
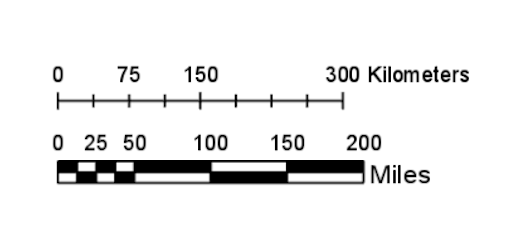
- Graphic Scale
- There is a bar line marked on the map to show how much actual distance is covered
- Mercator projection: This projection is often used for navigation because it preserves angles, which is useful for plotting a straight-line course. However, it distorts the size of land masses near the poles, making them appear larger than they actually are.
- Peters projection: This projection is designed to show countries in their true relative size, with minimal distortion. However, it distorts shapes and distances, making it less suitable for navigation.
- Equal-area projection: This type of projection preserves the area of land masses, but distorts shape and distance.
- The shape of an area can be distorted
- Distance between two areas is inaccurate
- The relative size of different areas is inaccurate
- Direction can be distorted
Okay, so there’s a good reason why maps aren’t as big as the actual area they are depicting. But how does a flat, 2D map on a piece of paper accurately represent our spherical Earth?
Let’s talk about projections.
A projection is a way of representing the curved surface of the earth on a flat map. Because the earth is a three-dimensional sphere, it is not possible to create a completely accurate flat map of the earth without distorting some of its features. Projections are used to minimize these distortions as much as possible, depending on the purpose of the map and the characteristics of the region being mapped.
There are many different types of map projections, each with its own set of strengths and weaknesses. Some common types of projections include:
It is important to choose the appropriate projection for the purpose of the map and the characteristics of the region being mapped. No single projection can capture all aspects of the earth's surface accurately, so trade-offs are always necessary.
Depending on what the cartographer wants to focus on, they have these four choices to make sure the globe fits on a paper:
Two Important Types of Projections:
Robinson projection
The Robinson projection is a type of map projection that was developed in the 1960s by Arthur H. Robinson. It is a modified version of the Mercator projection, which is commonly used for navigation. The Robinson projection is designed to reduce some of the distortions of the Mercator projection, particularly near the poles, while still preserving some of its useful properties.
The Robinson projection is a compromise projection, meaning that it tries to balance out some of the distortions inherent in all map projections. It is not a perfect projection, and it still distorts the size, shape, and distance of land masses in various ways. However, it is generally considered to be a more visually appealing and useful projection than the Mercator projection for many purposes, such as world maps and atlases.
The Robinson projection is commonly used for world maps and other maps that aim to show the entire earth or a large region. It is not typically used for smaller-scale maps, such as street maps, because it distorts shapes and distances too much for such purposes.
+ used to focus on oceans
- land masses are smaller
Image Courtesy of The Guardian
Mercator projection
The Mercator projection is a widely used map projection that was first introduced by the Flemish geographer and cartographer Gerardus Mercator in 1569. It is a cylindrical projection in which the meridians (lines of longitude) and parallels (lines of latitude) are straight and perpendicular to each other, creating a grid-like pattern on the map.
One of the main characteristics of the Mercator projection is that it distorts the size of objects as the latitude increases from the Equator to the poles. This means that objects near the poles, such as Greenland and Antarctica, appear much larger on a Mercator map than they actually are, while objects at the Equator appear smaller.
The Mercator projection is still widely used today, especially in online maps and navigation systems, because it is simple to construct and easy to use for activities such as plotting straight-line courses. However, it is not considered to be a particularly accurate representation of the Earth's surface, and other projections such as the Peters projection or the Gall-Peters projection have been developed to address this issue.
+ Accurate shape and direction
+ Map is rectangular
- Size of poles are distorted

Geographic Grid
There are imaginary grid patterns drawn on Earth’s surfaces that tell us specific locations.
Grid patterns are a type of spatial pattern that is characterized by a regular arrangement of objects or features in a grid-like structure. Grid patterns can be found in many different contexts, such as:
- Urban planning: Many cities and towns are laid out on a grid pattern, with streets and blocks arranged in a regular pattern.
- Agriculture: Some farming techniques, such as square foot gardening, involve planting crops in a grid pattern.
- Landscaping: Grid patterns can be used in landscaping to create a formal, structured look.
- Computer graphics: Grid patterns are commonly used in computer graphics to create structured backgrounds or to align objects.
Grid patterns are often used because they are simple and easy to understand, and they can be efficient in terms of the use of space. However, they can also be rigid and monotonous, and they may not always be the most aesthetically pleasing.
- Parallel: arcs in circles around the LAP of the earth
- Location of parallels is indicated by latitude
- LATitude → LAT=LAP= horizontal
- Your LAP is horizontal. So latitude is horizontal.
Latitude
Latitude is a measure of the location of a place on the earth's surface, expressed in degrees north or south of the equator. The equator is the imaginary line that runs around the earth's middle, dividing it into the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. Latitude is used, along with longitude, to specify the absolute location of a place on the earth's surface.
Latitude is measured in degrees, with the equator being at 0° latitude, the North Pole at 90° north latitude (written as 90° N or +90°), and the South Pole at 90° south latitude (written as 90° S or -90°). The latitude of a place is usually expressed as a single number, ranging from -90° at the South Pole to +90° at the North Pole.
Latitude is important because it determines the distance of a place from the equator, which in turn affects its climate, vegetation, and other characteristics. Latitude is also used in navigation, as it can be used to determine the position of a place relative to the equator and the North Pole.
- Meridian: arcs drawn from the North pole to the South pole
- Location of meridians is indicated by longitude
Meridian
A meridian is an imaginary line on the earth's surface that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole. It is used to measure longitude, which is the distance of a place east or west of the Prime Meridian. The Prime Meridian is an arbitrary reference point that has been established as the starting point for measuring longitude, and it is defined as 0° longitude.
Meridians are spaced evenly around the earth, with each meridian being about 69 miles (111 kilometers) apart at the equator. There are a total of 360 meridians, representing the 360 degrees of longitude. The International Date Line, which roughly follows a 180° longitude, is the meridian that marks the transition between one day and the next.
Meridians are important because they are used to determine the longitude of a place and its time zone. They are also used in navigation, as they can be used to determine the position of a place relative to the Prime Meridian.
- LONGitude → LONG= up and down
- If something is long, it is vertical. So longitude is vertical.
Longitude
Longitude is a measure of the location of a place on the earth's surface, expressed in degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian. The Prime Meridian is an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole, passing through the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England. Longitude is used, along with latitude, to specify the absolute location of a place on the earth's surface.
Longitude is measured in degrees, with the Prime Meridian being at 0° longitude, and the International Date Line, which roughly follows a 180° longitude, being at 180° longitude (written as 180° E or 180° W). The longitude of a place is usually expressed as a single number, ranging from -180° at the International Date Line to +180° at the Prime Meridian.
Longitude is important because it determines the distance of a place from the Prime Meridian, which in turn affects its time zone and the length of its day. Longitude is also used in navigation, as it can be used to determine the position of a place relative to the Prime Meridian.
🎥 Watch: AP HUG - Maps, Maps, Maps
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🗺Unit 1 – Thinking Geographically
👪Unit 2 – Population & Migration
🕌Unit 3 – Cultural Geography
🗳Unit 4 – Political Geography
👨🌾Unit 5 – Agriculture & Rural Land-Use
🌇Unit 6 – Cities & Urban Land-Use
💸Unit 7 – Industrial & Economic Development
🧐Exam Skills
📚Study Tools

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.