Unit 3 FRQ (Commercial Fertilizers) Answers
3 min read•june 18, 2024
AP Biology 🧬
358 resourcesSee Units
AP Bio Free Response Question Answers for Commercial Fertilizers
👋 Welcome to the AP Bio Unit 3 FRQ (Commercial Fertilizers) Answers. Have your responses handy as you go through the rubrics to see how you did!
⏱ Remember, the AP Biology exam has 6 free-response questions, and you will be given 90 minutes to complete the FRQ section. (This means you should give yourself ~15 minutes to go through each practice FRQ.)
Setup
Quality proteins are required for optimal health. In the healthcare and fitness industries, different protein powders are often used to meet nutritional standards or to maximize muscle growth and development. Protein powders may be manufactured from dairy or vegetable sources, including whey, casein, soy, and peas. The following table (Table 1) demonstrates five different types of protein powders, including a blend of all four.
Table 1
Questions with Answers & Rubric
(a) Identify the macromolecules supported by fertilizers containing high percentages of nitrogen and phosphorus.
🏆 1pt: Identify
- Proteins (aka peptides), nucleic acids
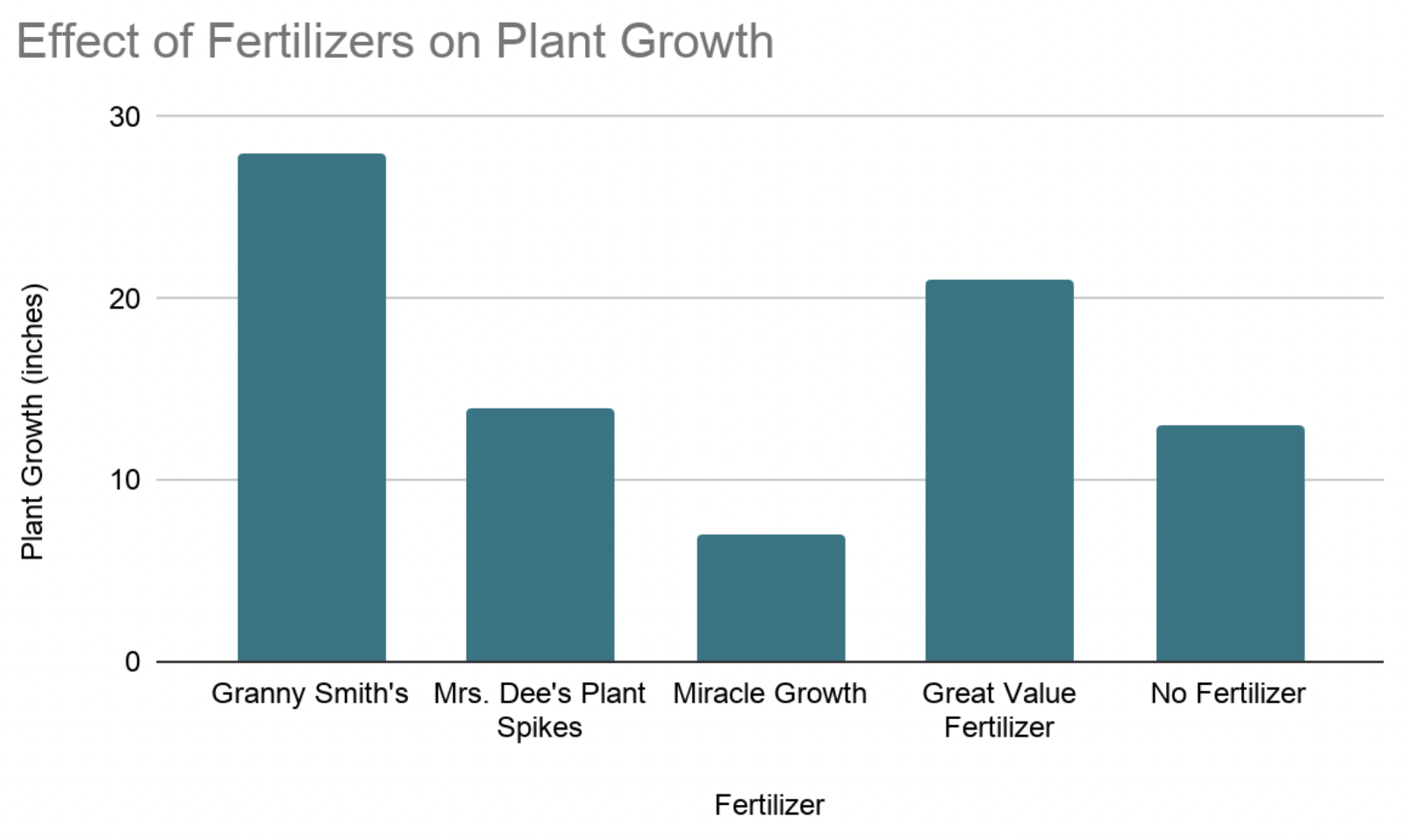
(b) Using the below graph, predict which fertilizer has the lowest concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus. One of the fertilizers has approximately half the amount of nitrogen and phosphorus of Granny Smith’s. Propose which fertilizer this is.
🏆 1pt: Predict
- Miracle Growth
🏆 1pt: Propose
- No Fertilizer
(c) An indoor greenhouse loses power, and while the building is appropriately insulated to maintain temperature and has appropriate airflow, there is no light. Tomato plants in the greenhouse utilize the energy and electron-carriers generated from the light-dependent phase of photosynthesis to generate glucose. However, after about a day, there is not enough energy left to continue any photosynthesis at all. Explain why the lack of light halts all photosynthesis after approximately twenty-four hours, instead of immediately.
🏆 3pts: Explain
- Part of photosynthesis is dependent on light (the light-dependent cycle) in which light must hit photosystems to excite electrons, which move through the electron transport chain to create a hydrogen gradient and generate electron carriers. These are stored up to a certain point, but deplete after a certain amount of time with no light. The electron carriers are used in the other cycle to generate ATP, so once they run out and there is no light, both processes are halted.
📄 Additional Resources
(d) Organisms living at the bottom of the ocean survive in a very hostile environment without light energy to power their metabolic foundation. However, microorganisms living near hydrothermal heat vents have managed to survive using an alternative method to photosynthesis. They harvest energy from the heat of the hydrothermal vents to manufacture their own food and supply the food chain above them. Name and describe the metabolic method used by microorganisms at the bottom of the ocean that is powered by hydrothermal vents.
🏆2pts: Describe
- Chemosynthesis is a metabolic pathway to generate energy independently. It is used by chemoautotrophs to generate energy using alternative sources than light, including sulfur. This creates food for the organism which can be accessed via cellular respiration.
Next Steps
- 🧠 Want to continue reinforcing your knowledge of Unit 3? Check out Unit 3 Trivia, either as a document or as a game.
- ⏭ Ready to move on to the next topic? Take a look at the collection of Unit 4 Resources.
- 📚 Want to review multiple units? Check out all of the AP Bio FRQs.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🧪Unit 1 – Chemistry of Life
🧬Unit 2 – Cell Structure & Function
🔋Unit 3 – Cellular Energetics
🦠Unit 4 – Cell Communication & Cell Cycle
👪Unit 5 – Heredity
👻Unit 6 – Gene Expression & Regulation
🦍Unit 7 – Natural Selection
🌲Unit 8 – Ecology
📚Study Tools
🧐Exam Skills

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.